Introduction
Many of us want to keep updated with the latest technology and block chain is one such new technology that is difficult to understand because of it's complexity. I tried to put it in as simple words as possible.
Block Chain
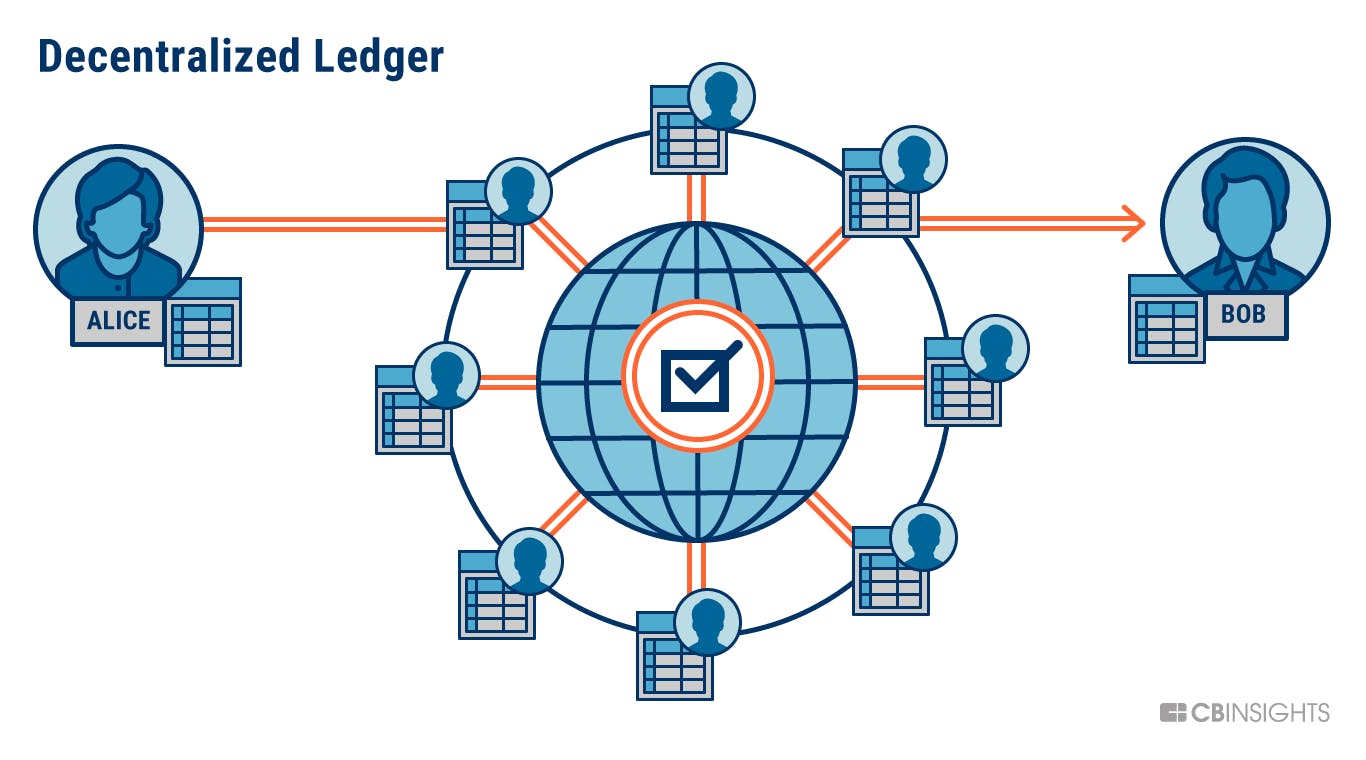
- Block chain is a ledger ( a ledger is something that keeps track of transactions ). But it is decentralised. Continue reading to understand more.
- Since it is a ledger, it also keeps track of transactions. So, it needs to store data about those transactions. More about transactions later.
- Block chain is a database which has some special features which make it special. Let's see what these special features are.
 Pic credits: LearnWeb3 DAO
Pic credits: LearnWeb3 DAO
Features of Block chain
Distributed : The data stored in the block chain is not present at only one place, instead it is distributed among all the nodes that are involved in the block chain network.
Shared : No individual has the total ownership or control over the block chain. The ownership of the block chain is shared between all the participants in the block chain. That is why it is decentralised. If any individual has that power, then it becomes centralised too which is not the purpose of block chain.
Permanent : The block chain or the data on block chain is permanent unless all the nodes of the block chain decides to delete the data from them at a time.
What is stored in a block chain ?
We know that block chain is a database by now. But what type of data does it store? We can store any data that can be digitally represented.
- We can store text, image, audio, video on block chain as all these can be converted into binary form.
- We can store the ownership of the items or data that is already on block chain.
- Contracts are also can be stored on block chain. These are called smart contracts. They help in making transactions when a particular event happens automatically.
How is data written on a block chain (transactions) ?
- Everything happening on a block chain is considered as a transaction.
- It can be adding data, modifying data, changing the ownership of data. Each of these tasks is considered as a transaction.
Block
- A block is a set of transactions.
- Every block has a fixed size depending on the block chain.
- The block is filled with transactions until it is full.
- Once the block is full, it is added to the block chain and a new block is created.
Miners
- A node which checks the transactions of a block and verifies them according to the proof of work and adds it to the block chain is called miner node and the person who does this is called miner.
- To mine the blocks, it requires a lot of computational power.
- That is why miners receive some amount to mine the blocks as an incentive.
- It involves some cryptographic calculations to mine blocks.
- A numerous miners try to mine a block simultaneously. But whoever does it first, gets the incentive.
- The incentive received by miners is from the transaction fee or gas fee associated with each transaction.
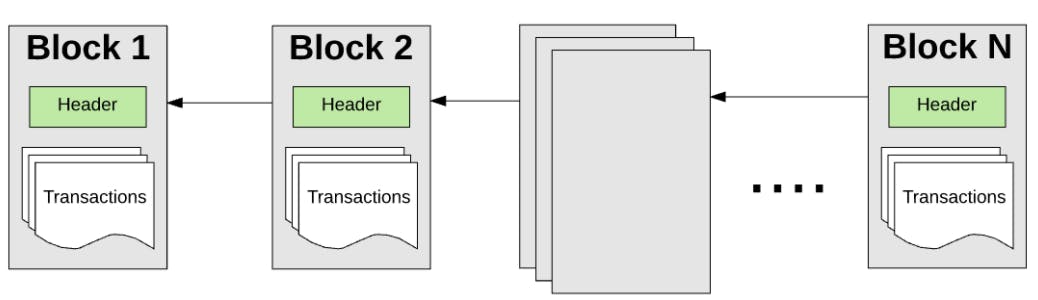
Chain
- Every block contains the hash value of data present in the previous block.
- This helps in maintaining the authenticity of the block chain.
- If someone wants to tamper the data in a block in the chain, every block from that point gets affected as the hash of data of previous block is present in every block and that hash value gets changed whenever the data is changed even slightly.
 Pic credits: LearnWeb3 DAO
Pic credits: LearnWeb3 DAO
State management
- A state is the current structure of the block chain.
- The state of the block chain changes with every block getting included and remember that block is set of transactions.
- The initial state of a block chain is called Genisis state.
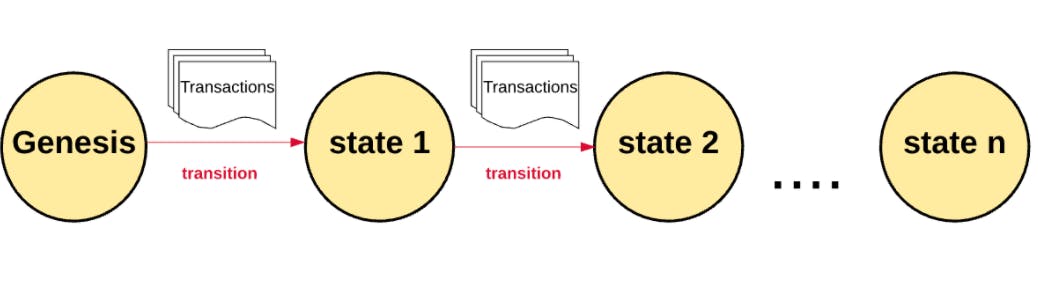 This is a pic depicting how the state transition happens in block chain.
Pic credits: LearnWeb3 DAO
This is a pic depicting how the state transition happens in block chain.
Pic credits: LearnWeb3 DAO
Authencticity of block chain
- Whenever a node processes a transaction, it is mined by miner node and the miner node sends the new block to the all other nodes so that all the nodes can add new block to the block chain in their local machine.
- There is a chance of doing bad practices when it is all decentralised. But consensus algorithm makes sure that these things can't be happened.
- A consensus algorithm is a common agreement which provides the rules on how to depict the authenticity of the block chain agreed by all the nodes of network.
Conclusion
We can go to a lot of depth on each of these words and topics. Surely will do that in future articles. That's it for this one.
Make sure you follow me on


